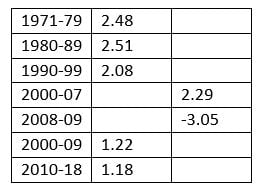
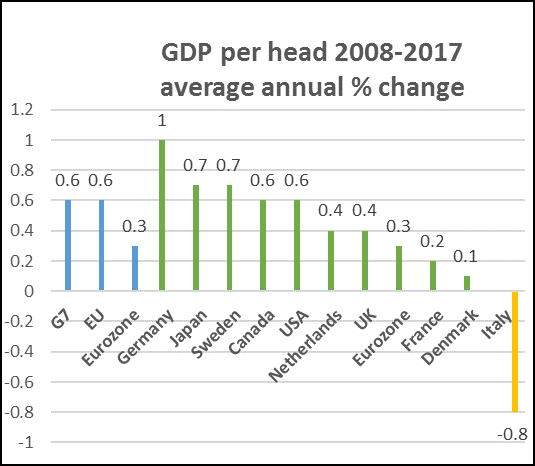
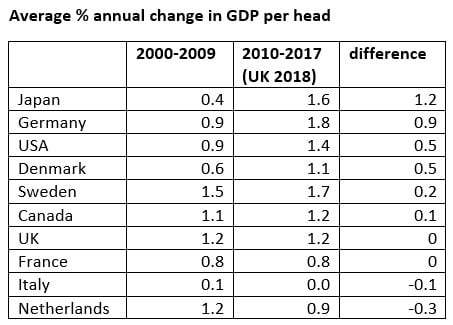
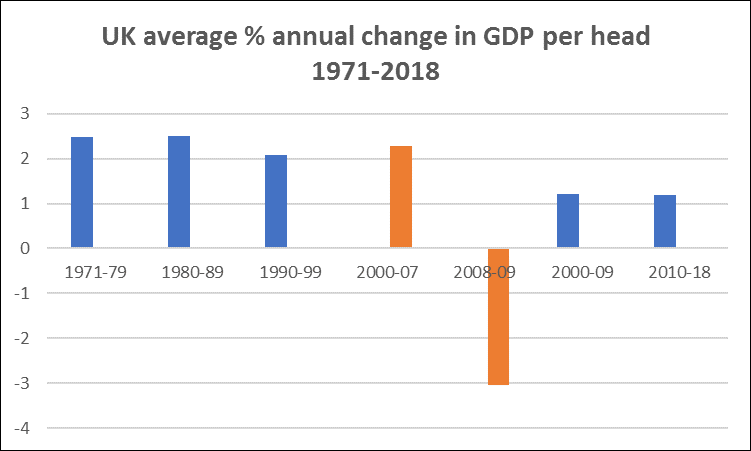In addition, I have compared the GDP per head figures for all of the above countries over the period 2000-2009, and 2010 to 2017 (the latest I have for all except UK, for which we have 2018), which are in the following Table. So the first period includes the damage caused directly by the Great Financial Crisis. What the Table shows is that the UK and Eurozone countries (except for Germany) have fared worse than the other countries in comparing the second period (2010-17) with the first:
The UK has fallen back from being second equal in the first period (even allowing for the crisis), to being now 5th equal. The Eurozone, of course, went through a double crisis – the Great Financial Crisis, followed by its own self-generated Eurozone crisis .
Towards the Spring Statement
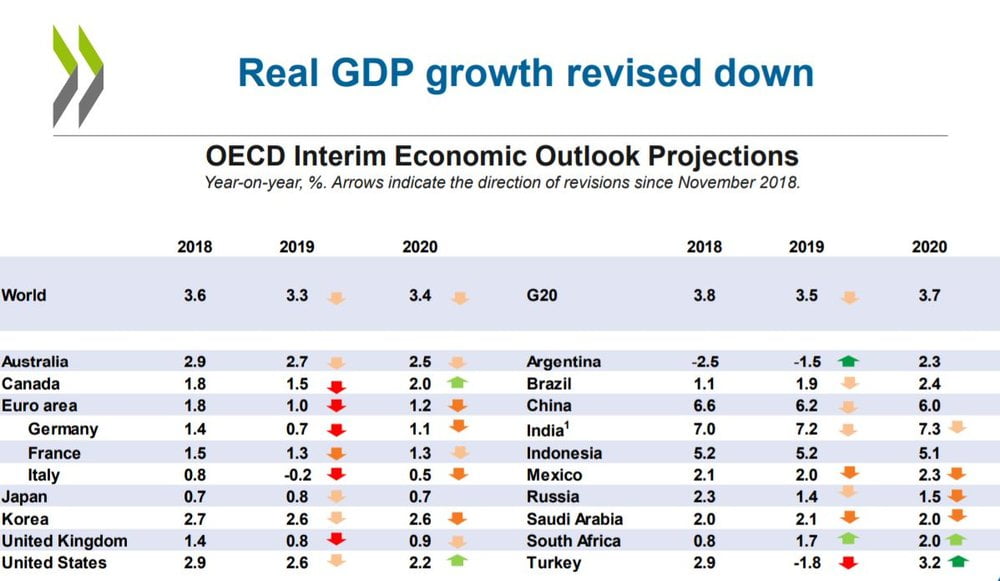
Yesterday (6 March) the OECD gave its Interim Economic Outlook projections. Its Chief Economist, Laurence Boone, was in gloomy form, marking down the world economy, but notably the UK and Eurozone ecopnomies. The UK, as you will see from their slide here, is now expected to “grow” by just 0.8% this year (down from its November estimate of 1.4%), and only 0.9% next year (2020).
Image and data with acknowledgment to OECD
The Chancellor’s Spring Statement is due next Wednesday (13th March) Even by Conservative economic logic, there can be no excuse but to increase public spending substantially and restore our rapidly decaying public services. The projection for the budget deficit this financial year (soon to end) is just over 1% of GDP. This means there is no good reason why this should not be increased.
The main fiscal rule that Chancellor Hammond set himself, back in 2016, is “to reduce cyclically-adjusted public sector net borrowing to below 2% of GDP by 2020-21“, and to see public debt as a percentage of GDP falling in 2020-21. However, he has given himself an escape clause:
In the event of a significant negative shock to the UK economy, the Treasury will review the appropriateness of the fiscal mandate and supplementary targets as a means of returning the public finances to balance as early as possible in the next Parliament.
While Mr Hammond’s “Charter” of Fiscal Responsibility” has not defined “a significant negative shock”, George Osborne’s earlier Charter had done so – real GDP annual growth forecast by the OBR to fall below 1% . So now the OECD has come in with a forecast of GDP increases of less than 1% over the next 2 years., which opens the gate wide to urgent fiscal action.
The target of overall budget “balance” or (worse) budget surplus has never been sensible or necessary given the UK’s circumstances, including the low cost of government borrowing, the need to revive public services and prepare the country for the future. But the Chancellor can now use his own escape clause to liberate us from the shackles of a perversely tight fiscal policy.
If public spending is increased by £40 billion a year, this would amount to less than 2% of GDP. This would give rise to a deficit of around 3% of GDP next year (taking into account the likely outturn this year). For a crisis like Brexit, that is a modest cost. Gross public investment is set to be 4.1% of GDP, so an overall 3% deficit would be in accordance with the Labour Party’s own “fiscal rule”. which allows for borrowing for investment And as we know, well targeted public spending has its own multiplier effect, which would have a positive impact at least from the following year.
We can now see and show, beyond any doubt, that the Conservative Age of Austerity has been a disastrous , historic economic failure. Whatever happens next with Brexit, it’s time for a radical change in economic policy.
It’s time for Government to use the full force of fiscal stimulus, to invest in our country’s future – in our infrastructure, our health, our education, our security – and to start on our generational task: the great transformation to the post-carbon era.
Jeremy Smith is co-director of PRIME. This article was first posted on 6th March in short form; it has been substantially reivsed and added to on 7th March.